Polymers
A polymer is a substance which is constructed from a large number of smaller monomer units. Addition polymerisation is used in the manufacture of many polymers, starting from different monomers.
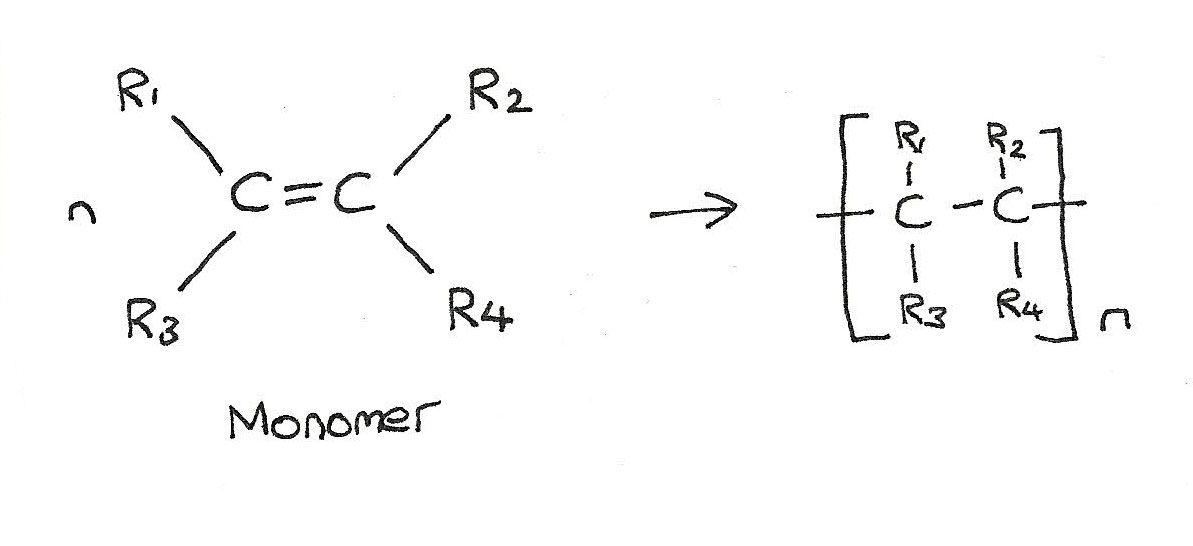
Addition Polymerisation
The process in which unsaturated alkene molecules (monomers) add to a growing polymer chain one at a time to form a long saturated chain.
Polymer Waste
Polymers have different uses:
- Poly(phenylthethene) / Polystyrene
This is a relatively cheap plastic that is used in packaging, insulation and in the food retail trade. - Poly(propene) / Polypropylene
This is used in food packaging and for containers that are dishwasher safe. In addition, it is also used as a material for chemical laboratory equipment, due to its resistance to chemical attack. - Poly(ethene) / Polythene
This is the most widely used plastic. It is used to make grocery bags, shampoo bottles and toys.
Addition polymers usually do not react with substances placed inside them and they are fairly durable and do not break down naturally. This causes problems in disposal.
Recycling
This is the reusing of plastics so that new raw materials do not need to be extracted to create more plastics. It involves two stages: sorting and reclamation.
- Sorting is the process of classifying recycled materials so that certain plastic can be used for certain purposes.
- Reclamation is the process of mechanically chopping a polymer into small flakes, before washing and then turning into new materials by melting and remoulding the pellets.
Other methods of disposal
- Burning polymers under controlled conditions produces heat energy, which can be harnessed to make electricity. This removes plastics from unsightly landfills.
- The conversion of polymers to synthesis gas is being investigated. These gases can then be used as chemical feedstock or as fuel at oil refineries.
Biodegradable polymers
Biodegradable polymers are plastics that have been derived from renewable raw materials such as starch, maize and lactic acid. Bioplastics are manufactured by non-hazardous processes and are less harmful to the environment as they degrade naturally when disposed.