Materials
Density
The density of a substance is defined as the mass per unit volume. It can be calculated using the formula:
$$ \rho = \frac{m}{V} $$
Where $\rho$ is the density measured in $kgm^{-3}$, $m$ is the mass measured in $kg$, and $V$ is the volume measured in $m^{3}$.
An unknown substance can be identified if its density is measured and compared to the density of known substances. c
- For a regular solid, the mass can be measured along with the dimensions. The formula can then be used with the measurements.
- For a liquid, the mass of the empty cylinder and the cylinder with the liquid should be measured. The volume of the liquid should be measured. By subtracting the mass without the liquid from the mass with the liquid, the volume can be determined. The density formula can then be used.
- For irregular solids the mass of the object can be measured, then the object should be immersed in liquid. When this is done, the increase of fluid level should be measured. This is the volume of the object. The density can then be calculated with the mass and volume.
Density of alloys
An alloy is a solid mixture of two or more metals. The density of the alloy can be found by dividing the mass of both metals by the volume.
$$ \rho = \frac {\rho_{A}V_{A} + \rho_{B}V_{B}}{V} $$
Hooke's Law
Hooke's Law states that the force needed to stretch a spring is directly proportional to the extension of the spring from its natural length. Hooke's Law may be written as:
$$ F = k \Delta L $$
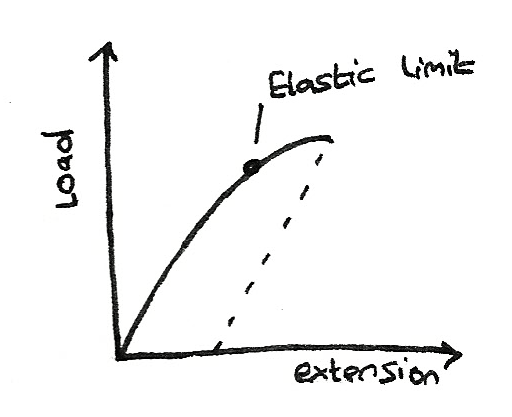
Where $k$ is the spring constant, and $\Delta L $ is the extension. The greater the value of $k$, the greater the force required to stretch the spring. If a spring is stretched beyond its elastic limit, it is unable to regain its original length.
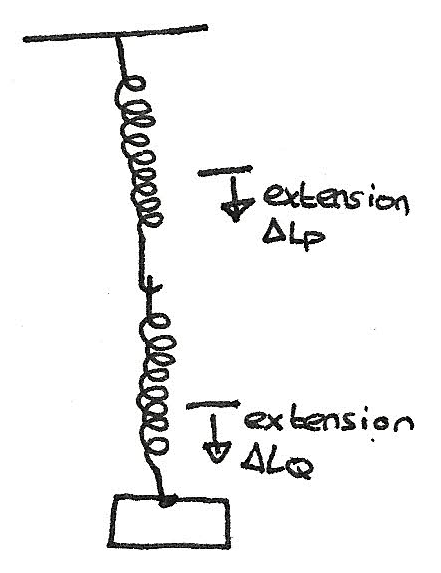
Springs in Parallel
As the weight is supported by both of the springs, the weight:
$$ W = F_{P} + F_{Q} = k_{P}\Delta L + k_{Q}\Delta L $$
With the effective spring constant as:
$$ k = k_{P} + k_{Q} $$
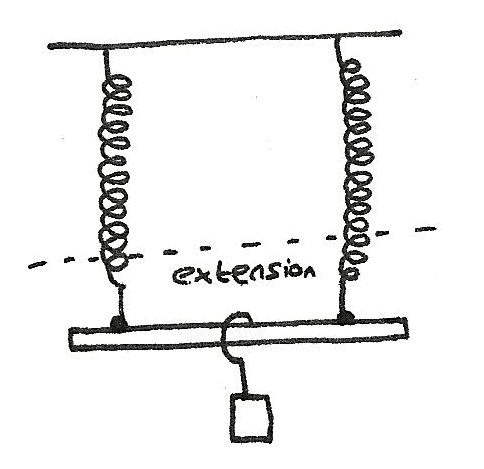
Springs in series
For springs in parallel, the extension of the springs is not equal, although the tension in each spring is the same. This means that the total extension is:
$$ \Delta L = \Delta L_{P} + \Delta L_{Q} = \frac {W}{k_{P}} + \frac {W}{k_{P}} $$
The effective spring constant is:
$$ \frac {1}{k} = \frac {1}{k_{P}} + \frac {1}{k_{Q}} $$
Energy stored in a stretched spring
Elastic potential energy is stored in a stretched spring. If the spring is released, the elastic potential energy is suddenly converted into kinetic energy. The elastic potential energy can be calculated by:
$$ E_{P} = \frac{1}{2}F \Delta L = \frac{1}{2}k \Delta L^{2} $$
Deformation of solids
The elasticity of a material is its ability to regain it's shape after been stretched. Deformation that stretches an object is tensile while deformation that compresses an object is compressive.
Stress
Tensile stress is a measure of the force per unit area of a material.
$$ \sigma = \frac{T}{A} $$
Where $\sigma$ is the stress measured in $Nm^{-2}$, $T$ is the tension and $A$ is the cross sectional area.
Strain
Tensile strain is defined as the extension per unit length.
$$ \epsilon = \frac{\Delta L}{L} $$
Where $\epsilon$ is the strain with no units as it is a ratio. Both $\Delta L$ and $L$ must use the same units.
Stress and Strain of a wire
Below is a graph showing the stress against strain for a wire.
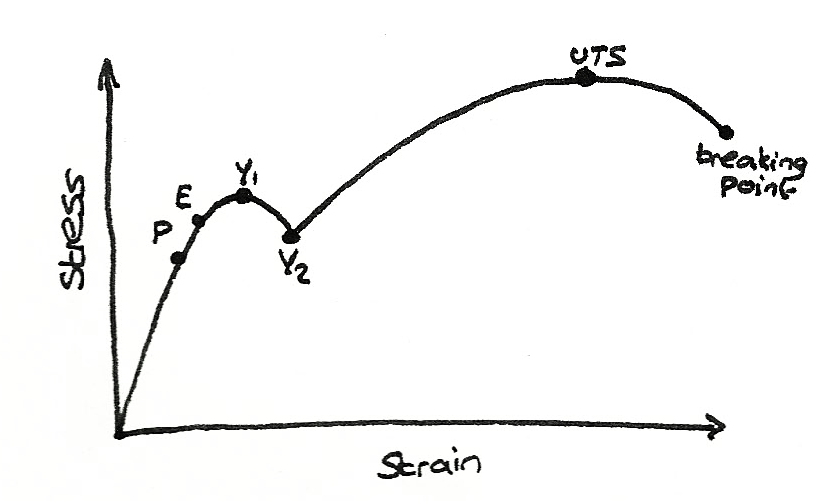
Between the origin and the limit of proportionality P, the strain is proportional to the stress. This means that at this stage, it has a constant Young modulus.
$$ \text{Young modulus} = \frac {\sigma}{\epsilon} $$
Once it passes the elastic limit, the point of which the wire is permanently stretched, and reaches the yield point $Y_{1}$, it weakens temporarily. Beyond $Y_{2}$, plastic flow occurs before reaching the ultimate tensile stress where the wire starts to become thinner and break.
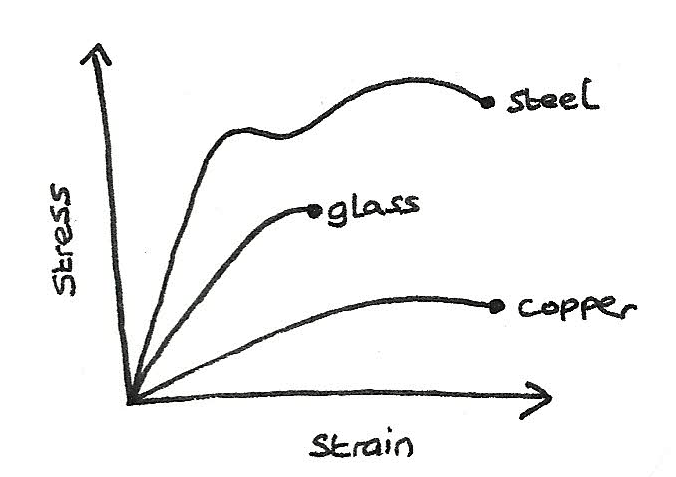
Stress-strain curve
The stiffness can be determined by calculating the gradient of a stress-strain line which is the Youngs Modulus. The greater Youngs Modulus is, the stiffer the material is.
- The strength of a material can be compared by the ultimate tensile stress. The greater the UTS, the stronger the material.
- A brittle material breaks without any noticeable yield. A ductile material is able to be drawn into a wire.
- A ductile material is able to be drawn out into a wire without breaking.
Loading and Unloading
- For a metal wire which obeys Hooke's Law, the unloading and the loading curves will both be straight lines. If the elastic limit is overcome, permanent extension will occur and the wire won't return to its original length.
- A rubber band is able to return to its original length when it is unloaded. However, the unloading curve always sits beneath the loading curve. This is due to it having a low limit of proportionality.
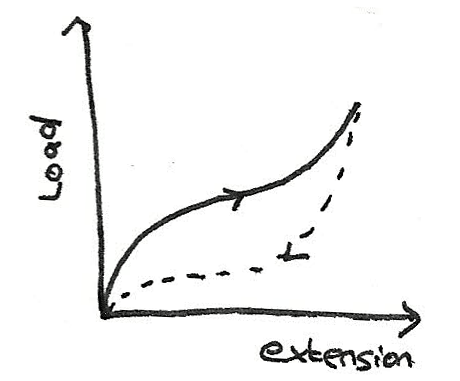
The area below the loading curve is the work done to stretch the band. The area below the unloading curve is the work done when it is unloaded. The area between the lines is the energy stored as internal energy in the molecules.
- A polythene strip is unable to return to its original length when it is unloaded. This is because polythene suffers from plastic deformation and a low limit of proportionality.
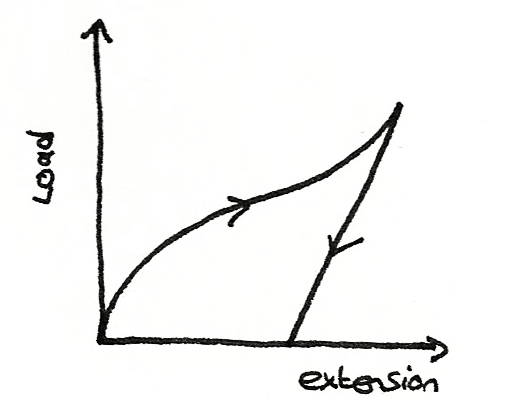
The area between the loading the unloading curves represent the work done to deform the material permanently.